Understanding the Complexity of Semaglutide Administration in a Home Setting
Semaglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, has revolutionized weight management and type 2 diabetes care due to its efficacy and safety profile when administered correctly. However, transitioning from clinical supervision to home administration demands precise knowledge and adherence to protocols to mitigate risks and optimize therapeutic outcomes. This article delves into the advanced procedural nuances and safety considerations essential for self-administering semaglutide injections at home, ensuring patient empowerment without compromising clinical rigor.
Optimizing Injection Technique: Anatomy, Site Selection, and Dosage Precision
Expert clinicians emphasize that the efficacy of semaglutide injections is intricately linked to the correct choice of injection site and technique. The preferred subcutaneous sites include the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm, each with unique anatomical considerations affecting absorption kinetics. For instance, the abdomen generally offers faster absorption due to richer vascularization but requires rotation to prevent lipodystrophy. Dosage accuracy is paramount; patients must use calibrated pens or prefilled syringes and adhere strictly to prescribed increments to avoid hypoglycemic events or gastrointestinal side effects.
What Are the Advanced Safety Measures to Prevent Common Injection-Related Complications?
Preventing injection site reactions such as erythema, swelling, or infection involves more than just sterile technique. Professionals recommend a regimen of site rotation, skin cleansing with alcohol swabs, and avoiding areas with scars or lesions. Additionally, patients should be educated on recognizing signs of adverse effects promptly. Advanced safety protocols include using needle guards, proper disposal of sharps, and maintaining a log to monitor injection sites and reactions over time. These measures are critical, especially for long-term semaglutide users, to sustain treatment adherence and safety.
Integrating Clinical Insights into Home Administration: Monitoring and Dose Adjustment
Home administration does not negate the need for continuous clinical oversight. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels, weight, and potential side effects is essential. Patients should maintain communication channels with healthcare providers to adjust dosing schedules based on therapeutic response and tolerance. Emerging evidence supports the use of telemedicine consultations to reinforce adherence and detect complications early, reflecting a paradigm shift in chronic disease management. Expert guidelines on safe dosage and monitoring provide structured frameworks for patients and clinicians alike.
Emphasizing Sterility and Storage: Pharmacological Integrity Outside Clinical Settings
The pharmacodynamics of semaglutide necessitate strict adherence to storage conditions to preserve molecular stability. Refrigeration between 2°C and 8°C is critical prior to first use, with room temperature storage permissible for limited periods post-opening. Patients must be trained on identifying signs of degradation such as discoloration or precipitates. Sterility protocols extend beyond needle hygiene to include the careful handling of injection pens and avoidance of contamination, aligning with standards set forth by pharmacological regulatory bodies.
Call to Action: Elevate Your Practice with Comprehensive Semaglutide Administration Knowledge
For clinicians and patients seeking to deepen their understanding of semaglutide’s role in weight management and diabetes control, explore our detailed Complete Semaglutide Injection Guide for Safe Use at Home. Engage with a community of experts to share clinical experiences and enhance patient safety protocols.
Reference: Drucker DJ. Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Application of Glucagon-like Peptide-1. Cell Metabolism. 2018;27(4):740-756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2018.03.001
Understanding Patient Education: Empowering Safe Practice Beyond Clinical Walls
One of the critical factors ensuring the success of semaglutide therapy at home is comprehensive patient education. Beyond simply providing instructions, healthcare professionals must equip patients with robust knowledge about the pharmacology, potential side effects, and emergency responses associated with semaglutide injections. This empowerment fosters adherence and confidence, significantly reducing the risk of misuse or adverse events.
Educational materials should include detailed visual aids, demonstration videos, and interactive sessions that cover injection techniques, site rotation protocols, and troubleshooting common issues like needle clogging or injection pain. Moreover, patients benefit from understanding the significance of lifestyle modifications complementing the medication’s effect, such as diet and exercise adjustments, which enhance weight management outcomes.
Advanced Monitoring Technologies: Integrating Digital Health Tools for Optimal Outcomes
Modern weight management strategies increasingly incorporate digital health technologies to monitor semaglutide therapy remotely. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices, paired with mobile health applications, provide real-time data analytics on glycemic control and symptom tracking. This integration enables clinicians to make timely dose adjustments and intervene early in the case of adverse reactions.
Telemedicine platforms further enable synchronous consultations, fostering a dynamic feedback loop that supports patient engagement and safety. These technologies also facilitate detailed adherence tracking, ensuring that injections are administered correctly and consistently, which is paramount for achieving expected therapeutic benefits.
How Can Personalized Dose Titration Protocols Improve Semaglutide Treatment Safety and Efficacy?
Personalized dose titration is fundamental in balancing semaglutide’s potent effects with patient tolerability. Clinicians tailor titration schedules based on patient-specific factors such as weight, metabolic profile, and history of gastrointestinal sensitivity. Initiating treatment at low doses and gradually increasing allows the body to adapt, minimizing side effects like nausea or vomiting.
Recent clinical insights underscore the value of individualized protocols over fixed regimens, optimizing both efficacy and safety. This approach requires meticulous patient monitoring and open communication channels to promptly address any emergent concerns. Healthcare providers can utilize decision support tools and standardized algorithms to guide titration, ensuring evidence-based adjustments aligned with patient response.
Ensuring Quality Control: Recognizing and Preventing Medication Adulteration in Home Settings
Maintaining the pharmacological integrity of semaglutide outside the clinical environment is essential to treatment success. Patients must be vigilant in sourcing medications exclusively through certified pharmacies and avoid counterfeit products, which can compromise safety and efficacy.
Storage guidelines should be strictly followed; deviations can lead to degradation of the peptide, rendering it ineffective or potentially harmful. Patients should regularly inspect injection pens for discoloration, sediment, or unusual odors. Educating patients on the risks of medication adulteration and counterfeit products strengthens the overall safety net surrounding home administration.
Exploring Drug Interactions and Contraindications in Home-Use Semaglutide Therapy
Semaglutide’s pharmacokinetic profile requires careful consideration of concurrent medications and patient comorbidities. For instance, concomitant use with other glucose-lowering agents necessitates dose adjustments to prevent hypoglycemia. Additionally, patients with personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma or Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 should avoid semaglutide due to potential risks.
Home users must communicate all medications and supplements with their healthcare providers to ensure safe co-administration. Regular reviews of patient health status and medication lists are recommended to preempt adverse interactions and contraindications.
Expert Perspectives: Incorporating Clinical Guidelines into Home-Based Semaglutide Use
Leading endocrinology associations emphasize integrating clinical guidelines with patient-centered care models for home semaglutide administration. The American Diabetes Association’s Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes highlights the importance of personalized treatment plans and continuous education. Source: American Diabetes Association, 2023 These frameworks support safe, effective, and sustainable weight and glycemic management outside traditional clinical settings.
Engage and Share: Enhancing Semaglutide Therapy Through Community Knowledge Exchange
Your experiences and insights with home-based semaglutide injections can provide invaluable guidance to others navigating this therapy. We invite you to share your questions, tips, or success stories to foster a collaborative learning environment. Additionally, explore our comprehensive resources like the Complete Semaglutide Injection Guide to deepen your understanding and optimize your treatment journey.
Precision Dose Titration: Tailoring Semaglutide Therapy to Individual Metabolic Profiles
Optimizing semaglutide therapy extends beyond standardized dosing schedules; it demands a nuanced approach tailored to each patient’s unique metabolic landscape. Precision dose titration considers variables such as baseline glycemic control, body mass index, gastrointestinal tolerance, and even genetic polymorphisms influencing GLP-1 receptor responsiveness. By adopting a patient-centric titration protocol, clinicians can finely balance the potent anorectic and glycemic effects of semaglutide against its common adverse effects, such as nausea and delayed gastric emptying.
Implementing such personalized regimens involves close monitoring through validated biomarkers and symptom tracking tools. For example, integrating continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) data enables dynamic dose adjustments that preempt hypoglycemia while maximizing glucose-lowering efficacy. Additionally, symptom diaries allow for real-time assessment of gastrointestinal side effects, facilitating timely intervention and dose modulation.
How Does Genetic Variability Affect Semaglutide Dose Optimization and Patient Response?
Emerging pharmacogenomic studies suggest that genetic differences in GLP-1 receptor expression and downstream signaling pathways can significantly affect semaglutide efficacy and tolerability. Polymorphisms in genes such as GLP1R and regulators of insulin secretion modulate patient responsiveness, thereby influencing optimal dose thresholds. Understanding these genetic underpinnings can guide clinicians in predicting which patients may require slower titration or alternative therapeutic strategies to minimize side effects and enhance treatment adherence.
While routine genetic testing is not yet standard practice, ongoing research underscores its potential in refining individualized treatment plans. Integrating genetic insights with clinical parameters will likely become a cornerstone of precision medicine approaches in diabetes and obesity management.
Complex Polypharmacy: Navigating Drug Interactions in Home-Based Semaglutide Use
Patients initiating semaglutide therapy at home often have comorbidities requiring multiple medications, raising concerns about drug-drug interactions that could compromise safety or efficacy. Semaglutide’s glucoregulatory effects may potentiate hypoglycemia when combined with insulin secretagogues or insulin itself, necessitating proactive dose adjustments and vigilant glucose monitoring.
Moreover, semaglutide slows gastric emptying, which can alter the pharmacokinetics of orally administered drugs. This effect requires careful consideration, particularly with narrow-therapeutic-index medications such as warfarin, digoxin, or certain antibiotics. Clinicians should evaluate the timing of drug administration relative to semaglutide injections and monitor for altered therapeutic responses.
Clinicians must also be alert to contraindications, such as a history of pancreatitis or thyroid C-cell tumors, which preclude semaglutide use. Comprehensive medication reconciliation and patient education on potential signs of adverse interactions are vital steps in mitigating risks in outpatient settings.
Leveraging Real-World Data and AI-Driven Decision Support for Enhanced Semaglutide Management
The integration of real-world evidence (RWE) and artificial intelligence (AI) into semaglutide therapy represents a frontier in optimizing home-based treatment. AI-powered platforms can analyze vast datasets encompassing patient demographics, lab results, and treatment outcomes to generate individualized dosing recommendations and predict adverse event risks.
Such tools empower clinicians to make data-driven decisions, augmenting traditional clinical judgment with predictive analytics. For patients, AI-enabled applications can provide personalized reminders, symptom tracking, and educational content, fostering adherence and early detection of complications.
However, the adoption of these technologies requires robust validation and addressing ethical considerations regarding data privacy and algorithmic transparency. Collaboration between healthcare providers, patients, and technology developers is essential to harness the full potential of AI in semaglutide management.
Reference: Nauck MA, Meier JJ. Incretin-Based Therapies: GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and DPP-4 Inhibitors in Type 2 Diabetes. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology. 2019;7(3):217–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30207-0
Call to Action: Deepen Your Expertise in Semaglutide Therapy Optimization
Healthcare professionals and patients alike are encouraged to explore advanced resources and engage with expert communities to refine semaglutide administration practices. Visit our Advanced Semaglutide Dosing Strategies Portal to access in-depth protocols, interactive case studies, and peer discussions that elevate your clinical acumen and patient outcomes.
Harnessing Pharmacogenomics for Tailored Semaglutide Regimens
The advent of pharmacogenomic profiling has ushered in a new era in personalized medicine, particularly for semaglutide therapy. Variability in the GLP1R gene and other related loci can modulate receptor sensitivity and downstream insulinotropic effects, thereby influencing both efficacy and adverse event profiles. Clinicians incorporating genetic insights can devise titration protocols that anticipate patient-specific tolerability thresholds, optimizing therapeutic windows while minimizing gastrointestinal disturbances.
How Does Genetic Variability Affect Semaglutide Dose Optimization and Patient Response?
Emerging evidence suggests that polymorphisms affecting GLP-1 receptor density and signaling cascade efficiency may dictate differential patient responses to semaglutide. Patients harboring specific allelic variants may exhibit either heightened sensitivity or resistance, necessitating bespoke dose escalation strategies. This pharmacogenetic knowledge base, though not yet mainstream in routine clinical workflows, promises to refine dose individualization and mitigate discontinuation rates due to side effects.
Navigating Complex Polypharmacy: Strategies to Mitigate Drug-Drug Interactions in Ambulatory Settings
Given that semaglutide users frequently present with multimorbidity requiring multiple concomitant medications, understanding the nuanced interplay between semaglutide and other drugs is critical. Semaglutide’s gastric emptying delay can alter absorption kinetics of orally administered therapeutics, including anticoagulants and narrow therapeutic index agents like digoxin. Proactive therapeutic drug monitoring and staggered dosing schedules are imperative to avert subtherapeutic exposure or toxicity.
Moreover, synergistic hypoglycemic risk when semaglutide is combined with sulfonylureas or insulin mandates vigilant glucose surveillance and judicious medication adjustments. Comprehensive medication reconciliation and patient education remain cornerstones of safe polypharmacy management.
Leveraging Real-World Evidence and AI-Driven Decision Support for Dynamic Semaglutide Management
The integration of real-world data analytics and artificial intelligence platforms represents a transformative approach to optimizing semaglutide administration. AI algorithms can synthesize multidimensional patient data—including continuous glucose monitoring metrics, adherence patterns, and side effect reports—to generate predictive models for dose titration and risk stratification.
These intelligent systems enable clinicians to preemptively identify patients at elevated risk of adverse events and tailor interventions accordingly, fostering precision medicine in outpatient contexts. Concurrently, AI-powered patient applications enhance engagement through personalized reminders and interactive educational modules, reinforcing treatment adherence and early problem detection.

Call to Action: Deepen Your Expertise in Semaglutide Therapy Optimization
We invite healthcare professionals and informed patients to explore our Advanced Semaglutide Dosing Strategies Portal – a hub for cutting-edge protocols, expert case discussions, and collaborative forums designed to propel your clinical acumen and patient outcomes to unprecedented levels.
Expert Insights & Advanced Considerations
Precision Dose Titration Enhances Therapeutic Outcomes and Minimizes Side Effects
Individualizing semaglutide dose escalation based on patient-specific metabolic profiles and tolerability parameters is indispensable for maximizing efficacy while reducing gastrointestinal adverse effects. Clinicians should leverage continuous glucose monitoring data and symptom tracking to fine-tune dosing schedules, rather than adhering strictly to fixed regimens, thus enhancing adherence and long-term success.
Pharmacogenomics Offers a Promising Frontier for Personalized Semaglutide Therapy
Emerging evidence indicates that genetic polymorphisms, particularly in the GLP1R gene, influence patient responsiveness and side effect profiles. Integrating pharmacogenomic insights into clinical decision-making could soon enable tailored titration protocols that anticipate individual tolerability thresholds, optimizing both safety and outcomes in semaglutide use.
Comprehensive Management of Polypharmacy is Crucial in Ambulatory Settings
Given semaglutide’s impact on gastric emptying and glucose regulation, careful review and timing adjustments of concomitant medications—especially those with narrow therapeutic indices—are essential to avoid suboptimal drug levels or heightened adverse effects. Clinical vigilance and patient education remain key to navigating drug-drug interactions safely.
AI-Driven Decision Support and Real-World Evidence Revolutionize Home-Based Care
Artificial intelligence platforms synthesizing multidimensional patient data facilitate dynamic dose optimization and early detection of adverse events. These technologies empower clinicians with predictive analytics and support patients through personalized reminders and educational content, advancing precision medicine paradigms in semaglutide therapy.
Patient Education and Empowerment Remain Central to Safe and Effective Home Administration
Beyond technical instruction, educating patients on pharmacodynamics, injection techniques, and symptom recognition fortifies treatment adherence and mitigates risks. Incorporating interactive tools and continuous support mechanisms fosters confidence and sustainable therapeutic engagement.
Curated Expert Resources
American Diabetes Association – Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes (2023): Provides authoritative, evidence-based guidelines emphasizing individualized GLP-1 receptor agonist therapy and patient-centered care models relevant for semaglutide administration.
Cell Metabolism – Mechanisms of Action of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists (Drucker DJ, 2018): Offers in-depth molecular and pharmacological insights underpinning semaglutide’s therapeutic effects.
The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology – Incretin-Based Therapies Review (Nauck & Meier, 2019): A comprehensive review of GLP-1 receptor agonists, including clinical applications, safety considerations, and emerging technologies.
Complete Semaglutide Injection Guide for Safe Use at Home (BestFastWeightLossDiets.com): A practical resource detailing protocols, injection techniques, and safety measures tailored to home settings.
Advanced Semaglutide Dosing Strategies Portal (BestFastWeightLossDiets.com): An interactive hub featuring expert case studies, dosing algorithms, and peer discussions to elevate clinical practice and patient outcomes.
Final Expert Perspective
Mastery of semaglutide administration at home transcends mere compliance; it demands a sophisticated integration of personalized dosing, vigilant polypharmacy management, patient empowerment, and innovative digital tools. The convergence of pharmacogenomics and AI-driven analytics heralds a new epoch in individualized therapy, promising enhanced efficacy and safety. Embracing these advanced insights ensures that semaglutide’s full potential in weight management and diabetes care is realized beyond the clinic’s confines.
Professionals and informed patients are encouraged to deepen their expertise by engaging with comprehensive resources such as the Complete Semaglutide Injection Guide for Safe Use at Home and actively contribute to community knowledge via platforms like the contact page. Collaborative learning and continuous advancement remain the cornerstones of optimizing semaglutide therapy in the evolving landscape of home-based care.

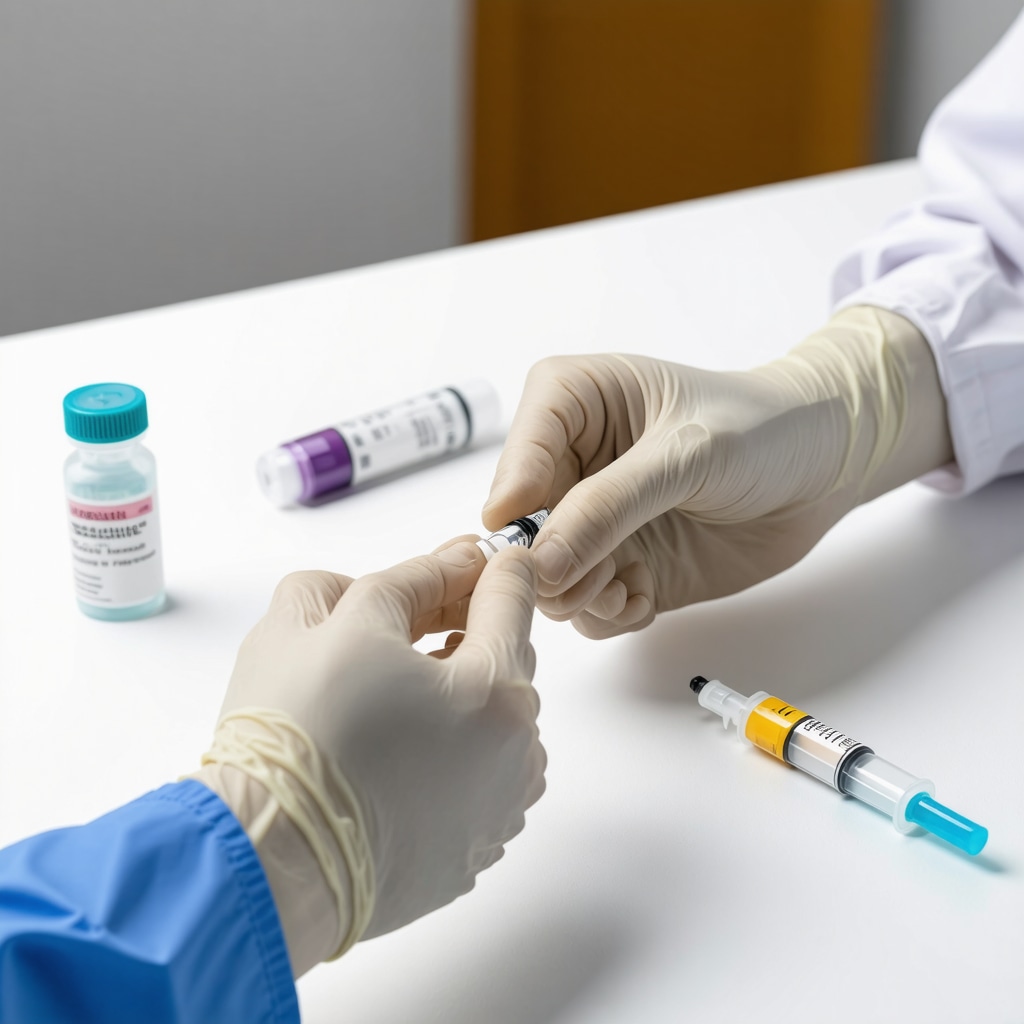
I found the detailed discussion on the importance of precise injection technique and site rotation particularly insightful. From my own experience trying semaglutide at home, ensuring consistent rotation between the abdomen and thigh really helped minimize local irritation and prevented any noticeable lipodystrophy. It’s interesting how the abdomen provides faster absorption due to its vascularization, but also poses a greater risk for skin issues without proper rotation. Also, the emphasis on dosage accuracy can’t be overstated—using calibrated pens and sticking tightly to prescribed doses drastically reduced my episodes of nausea, a common side effect I had initially struggled with.
What resonated with me as well is the need for continuous clinical oversight even when self-administering. Telemedicine visits have been invaluable for me to adjust doses based on glucose readings and side effect tolerance. Plus, keeping a detailed injection log helped me and my provider track any reactions systematically.
I’m curious how other patients have adapted their routines to maintain sterility and storage conditions, especially if refrigeration isn’t readily available or during travel? Sharing practical strategies could be a great addition to this conversation.
This article offers a comprehensive overview of the crucial aspects involved in safe semaglutide home administration, which is vital given its increasing use for weight management and T2D control. From my experience, the emphasis on site rotation and proper storage cannot be overstated. In particular, I’ve found that keeping an organized injection schedule and a dedicated storage location helps maintain medication integrity, especially during travel or power outages when refrigeration might be temporarily unavailable. Also, staying vigilant about signs of medication degradation, like discoloration, gives me peace of mind.
Regarding safety protocols, I would add that using a sharps disposal container and being meticulous about needle handling are simple yet effective measures to prevent injuries and contamination. Since many of us rely on telehealth, regular virtual check-ins to adjust doses based on blood glucose and side effects have been crucial for my ongoing treatment.
What are some best practices others have adopted for maintaining sterility and proper storage when traveling long distances or in areas with limited refrigeration options? Sharing these tips could greatly benefit others managing similar challenges.
This article touches on some critical points that resonate with my own experience managing semaglutide at home. I agree that consistency in injection technique, site rotation, and dosage accuracy are foundational for safe and effective treatment. What stood out to me was the emphasis on personalized care, like using CGM data to fine-tune dosing—something I’ve found to be incredibly helpful in preventing side effects while maximizing benefits.
In terms of storage and sterility, I’ve faced challenges during travel, especially in areas where refrigeration isn’t always accessible. I’ve started carrying insulated coolers with ice packs and always keep a dedicated injection kit to minimize contamination risks. Also, I stay vigilant for signs of medication degradation, like changes in color or texture.
I’m curious, have others found effective ways to maintain sterility and medication stability during long trips or in hot climates? Sharing practical tips could help improve safety practices across the community.